The slope of a straight line is commonly represented using the equation y = mx + b where m is the slope of the line. There is more on this here. This equation can be derived using any two points that lie on the line.
The slope formula lets us calculate the value, m, using any two such points.
As shown below, the slope, m is calculated by dividing the difference in the y-values by the difference in the x-values. This is often referred to as being the rise divided by the run.
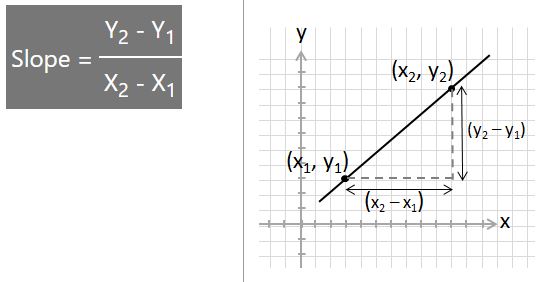
The formula states that the slope of a line is equal to the difference in y-values divided by the difference in x-values of two points on that line. This is also referred to as the rise divided by the run.
Examples Using the Formula
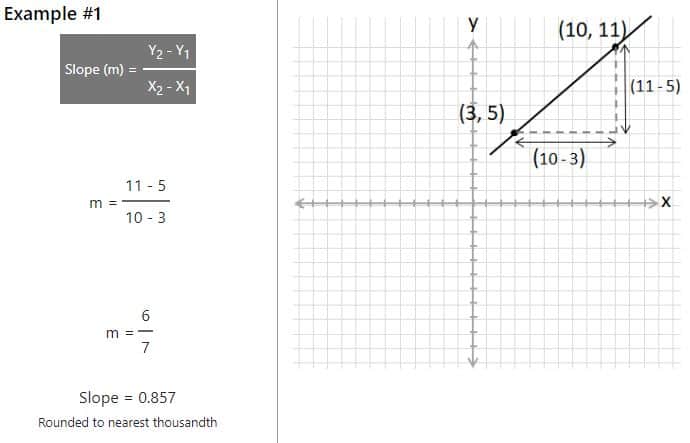
It does not matter which points on the line you take as being (X1, Y1) and which is (X2, Y2) as the example below using the same two points as Example #1.



Worksheets
Use the worksheet(s) below for practice.
- Calculating the Slope of a Line – using m = (Y2 – Y1)/(X2 – X1) (2-Pages)









